
Area is calculated using geometry, and is computed by splitting polygons into smaller, less complicated shapes, enabling swift and efficient calculation.
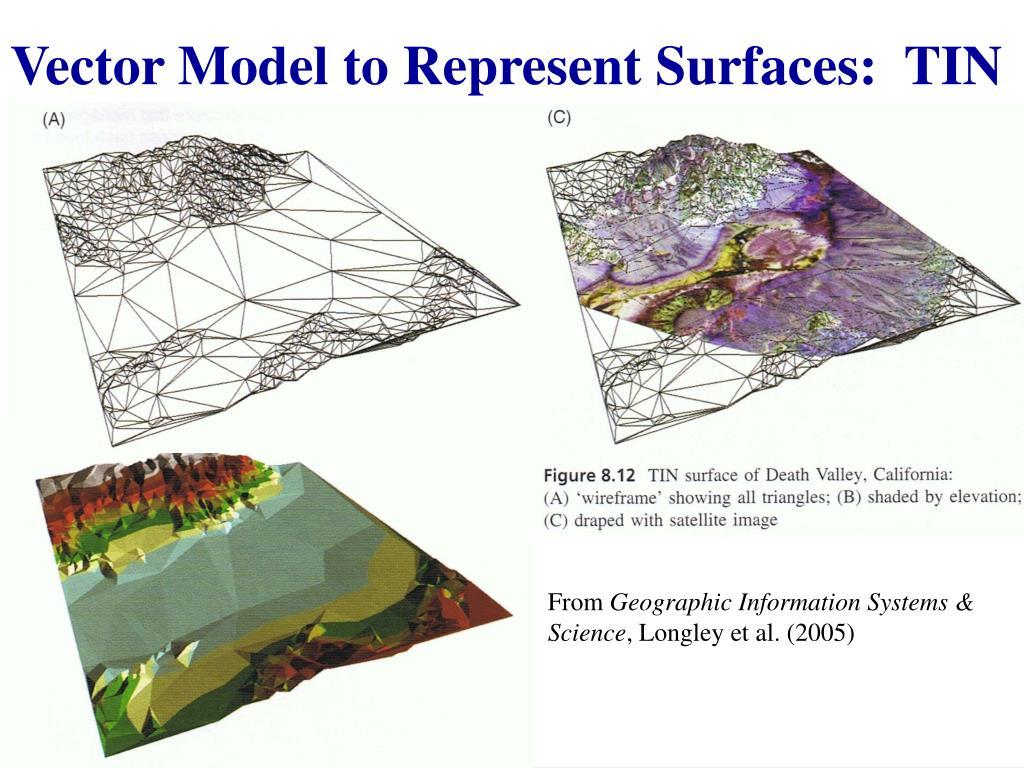
Vector models calculate Euclidean distance of lines and perimeters using Pythagorean theory (Heywood et al., 2011), based on explicit coordinate locations for each node. However, any comparison between models should be made based on utility.ĭifferences between the models become apparent when conducting fundamental spatial operations. Within current literature there is debate about the utility of vector compared with that of raster, with some asserting that vector’s accuracy is superior, and more appealing because its graphic similarity to paper maps. Vector models are stored through individual entities in the form of points, lines, and polygons, with raster comprising grid cells of a predefined resolution. Image Courtesy:ġ.”Figuur beschrijft fenomeen raster-data en vector-data bij inzoomen” By T.Nijeholt at nl.wikibooks (CC BY-SA 3.There are two main types of data models available to GIS: vector and raster. Buckey.” Module 4 – Water Hyacinth, Available here. Reference:ġ.“Help.” What Is SQL?-Help | ArcGIS Desktop, Available here.Ģ.Richard. The main difference between Raster and Vector Data is that the raster data represents data as a cell or a grid matrix while vector data represents data using sequential points or vertices. Raster data and vector data are two types of spatial data in GIS. However, administrative borders, linear features, roads, and rivers are some examples of vector data. Temperature, air pressure, soil PH, ecotones, elevation, flow, and distance are some example of raster data. Hence, this is also a difference between raster and vector data. Moreover, raster data is simpler than vector data. Data RepresentationĪnother difference between raster and vector data is that raster data represents data in cells or in a grid matrix whereas vector data represents data using sequential points or vertices. Importantly, while raster data is continuous data, vector data is discrete data. Thus, this is the main difference between raster and vector data. Whereas, vector data is a type of spatial data used for storing data that has discrete boundaries.

Raster data is a type of spatial data that consists of a matrix of cells organized into rows and columns in which each cell represents specific information. Difference Between Raster and Vector Data Definition Furthermore, it can be expensive to display high-quality colors. It is difficult to simulate them as each unit has a different topological form.
#Raster and vector data model in gis update#
Moreover, it is also possible to generalize and update raster data. It also helps to represent accurate graphics. It helps to describe the entire topology. Vector data provides multiple advantages. Moreover, vector data display latitude and longitude using lines, points, polygons, etc. Administrative borders, linear features, roads, and rivers are some examples of vector data. Each vertex contains x coordinate and a y coordinate. Vector data uses sequential points or vertices to represent data. Moreover, if there is no special hardware or algorithms, the projection transformations can be time-consuming. It can also be difficult to establish network linkages. On the other hand, raster data can cause information loss. They are easier to simulate as all the cells are of the same size and same shape. Chemical concentrations and elevation surface are some examples of raster data. Each cell has a value that represents information.

In other words, it is a matrix of cells organized into rows and columns. – Comparison of Key Differences Key Terms Difference Between Raster and Vector Data In brief, raster data is continuous data whereas vector data is discrete data. It is possible to maintain spatial data as vector data or raster data.

One data type or data structure available in GIS is spatial data. Users can visualize, and understand the relationships between geo data in forms of reports, charts, maps etc. Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer-based tool or technology to manage, analyze and display geographically referenced information. The main difference between raster and vector data is that the raster data represents data as a cell or a grid matrix while vector data represents data using sequential points or vertices.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
